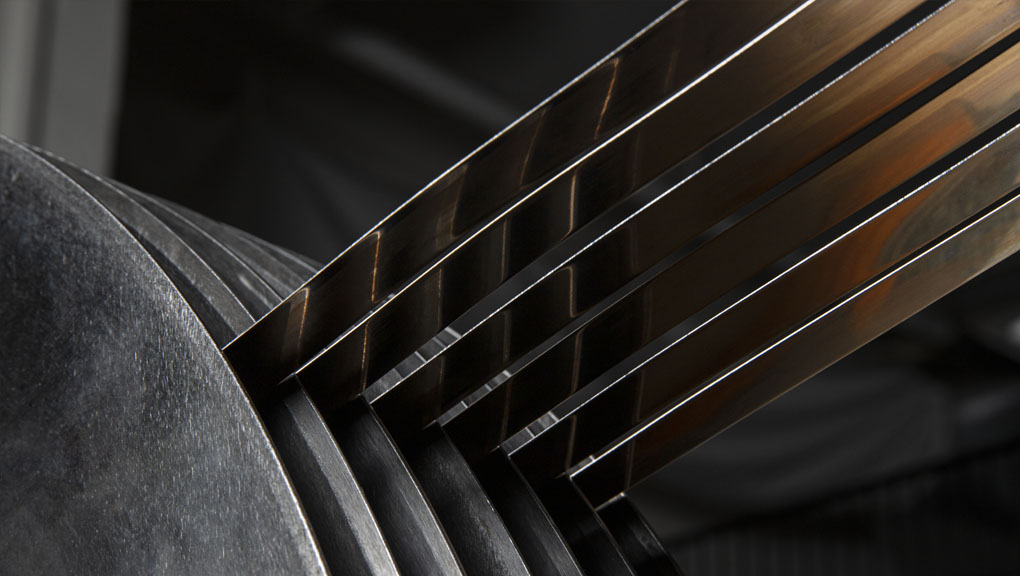
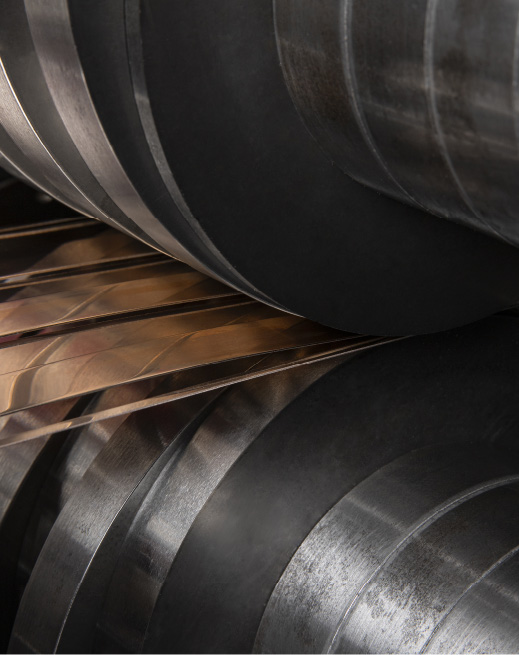
Depuis 1836, notre entreprise familiale ROBERT LAMINAGE fabrique avec la plus grande précision des bandes métalliques et des feuilles minces.
Nous sommes fournisseurs pour une très large palette d’alliage couvrant les besoins les plus exigeants de l’industrie. Nous avons également développé un savoir-faire unique dans la conception de solutions sur-mesure pour les applications spéciales.
- Solutions sur-mesure
- One stop shop
- Délais courts
- Taille de lot : 1kg à 5000kg
- Spécialisé dans les bandes et feuilles minces
- 700 tonnes de métal en stock
- Finition de surface spéciale "Finition poli"
- Ouvert aux demandes complexes
- Swiss made
- Critères strictes de Qualité, Durabilité et Environnement